Synthetic or non-nutritive sweeteners
“The majority of observational studies addressing synthetic or non-nutritive sweeteners (NNS) consumption show an association with metabolic dysregulation.”
Beyond food intake, numerous studies have shown…
animals consuming synthetic sweeteners exhibit weight gain
Feijó et al., 2013
Swithers and Davidson, 2008
Swithers et al., 2010
Swithers et al., 2013
impaired glucose homeostasis
Suez et al., 2014
Swithers et al., 2012
weaker caloric compensation
Swithers et al., 2010
synthetic sweeteners act through the microbiome
Suez et al., 2014
reduced validity of “sweetness” to predict caloric content
Swithers et al., 2010
significant correlation between NNS consumption and weight gain in an 80,000 participants study
Stellman and Garfinkel, 1988
Other independent studies confirmed these associations, with synthetically sweetened beverage consumption being associated with a much higher incidence of metabolic syndrome (odds ratio ∼1.93) when compared to non-users
Fowler et al., 2008
Lutsey et al., 2008
and NNS consumption has been identified as a significant risk factor for metabolic disease
in children
Blum et al., 2005
in middle-aged adults
Dhingra et al., 2007
and in the elderly
Fowler et al., 2015
One study showed that NNS consumers exhibit reduced weight gain
Schulze et al., 2004
however, these participants showed increased risk for developing diabetes in an 8-year follow-up.
Furthermore, human intervention studies have also shown that ingestion of NNS could
enhance appetite
Blundell and Hill, 1986
Rogers and Blundell, 1989
promote hunger
Tordoff and Alleva, 1990
and increase food consumption
Lavin et al., 1997
Rogers and Blundell, 1989
Tordoff and Friedman, 1989a
resulting in impaired glucose tolerance
Pepino et al., 2013
Suez et al., 2014
However, other studies have reported no major effect or weight loss as a result of consuming NNSs
De La Hunty et al., 2006
de Ruyter et al., 2012
Raben et al., 200
The overall impact of NNS on metabolic health remains controversial.
“Despite inclusion in thousands of products, and consumption by billions of people, the molecular effects of ingesting synthetically sweetened food are not well understood. Moreover, there is conflicting evidence from both human and animal studies as to whether or not synthetic sweeteners interact with overall physiology or regulation of energy homeostasis.”
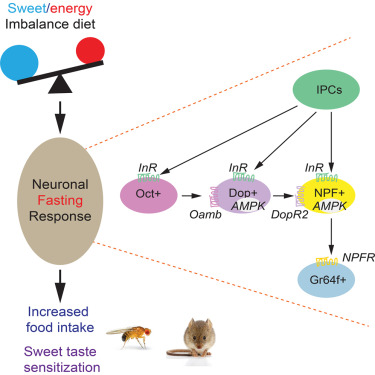
Excerpts from: Sucralose Promotes Food Intake through NPY and a Neuronal Fasting Response
All the studies referenced here are cited and hyperlinked in the article.



Recent Comments